Part B: 13-Mark Questions
1. Define phase rule. Draw the phase diagram of water system and explain in detail.
Phase Rule (Gibbs Phase Rule):
The equilibrium state of a system is expressed as:
Where:
- F = Degrees of freedom (independent variables)
- C = Components
- P = Phases
Phase Diagram of Water System:
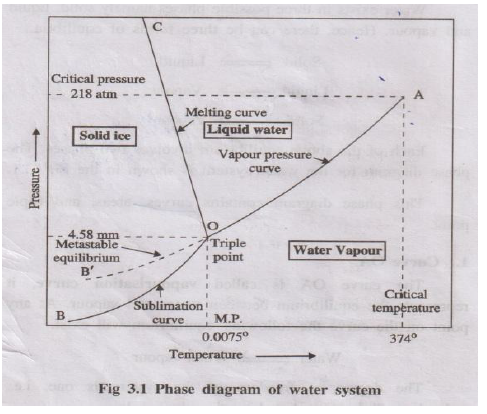
Water exists in 3 phases: Ice (solid), Liquid water, and Vapour.
- Curve OA (Vapourisation curve): Equilibrium between water and vapour. System is univariant (F=1).
- Curve OB (Sublimation curve): Equilibrium between ice and vapour. System is univariant (F=1).
- Curve OC (Melting curve): Equilibrium between ice and water. Melting point decreases with pressure. System is univariant (F=1).
- Point O (Triple Point): All three phases (Ice, Water, Vapour) are in equilibrium. System is non-variant (F=0). This occurs at 0.0075°C and 4.58 mm Hg.
- Metastable curve (OB'): Represents equilibrium between supercooled water and vapour.
Areas:
- Region AOC: Liquid water phase.
- Region BOC: Solid ice phase.
- Region AOB: Vapour phase.
In each single-phase area, the system is bivariant (F=2), meaning both temperature and pressure can be changed independently.
2. (i) Define phase, component and degrees of freedom with example. List out the limitations of phase rule.
- Phase (P): A homogeneous, physically distinct, and mechanically separable part of a system.
Example: In the H2O system, Ice (solid), water (liquid), and vapour (gas) are 3 distinct phases. - Component (C): The minimum number of independent chemical constituents required to express the composition of all phases.
Example: The H2O system has 1 component (H2O). The decomposition of CaCO3 (CaCO3 ⇌ CaO + CO2) has 2 components. - Degrees of Freedom (F): The minimum number of independent variables (like Temperature, Pressure, Concentration) that must be fixed to define the system's state.
Example: For the Water ⇌ Vapour equilibrium, F=1 (univariant). If you fix the temperature, the pressure is automatically set.
Limitations of Phase Rule:
- It is applicable only to systems in equilibrium.
- It considers only variables like Temperature, Pressure, and Concentration (ignoring electrical, magnetic, or gravitational forces).
- All phases must be present under the same conditions of temperature and pressure.
- It is not valid for very small (finely divided) quantities of solids or liquids, as surface tension effects become significant.
2. (ii) Explain thermal analysis / cooling curves in detail.
- Thermal Analysis: A technique of studying the solidification of molten systems by plotting cooling curves (Temperature vs. Time).
- Pure substance: A cooling curve for a pure substance shows a constant temperature plateau (a horizontal line) during solidification (freezing).
- Mixture: A cooling curve for a mixture typically shows two breaks:
- An initial break in the slope when the first solid component begins to separate.
- A horizontal plateau where the eutectic mixture solidifies at a constant temperature.
Uses:
- Determines the melting point of pure substances and the eutectic temperature of mixtures.
- Helps find the purity of metals.
- Used to derive phase diagrams for two-component (binary) systems.
3. What are composite materials? Discuss the important types of fibre reinforced composites.
Composite materials:
Engineered materials made by combining two or more distinct materials (a matrix and a reinforcement) to achieve superior properties (like higher strength-to-weight ratio) that are not attainable by any of the individual components alone.
Fibre Reinforced Composites (FRC):
These are composites where a matrix (like a polymer resin) is reinforced with fibres. The fibres carry the primary load and provide strength and stiffness.
Important Types of FRC:
- Glass Fibre Reinforced Plastics (GFRP): Uses glass fibres. Known for high strength, good electrical insulation, and low cost. Used in boat hulls, pipes, and automotive parts.
- Carbon Fibre Composites (CFRP): Uses carbon fibres. Known for being extremely strong, stiff, and lightweight. Used in high-performance applications like aerospace, racing cars, and sporting goods.
- Aramid Fibre (e.g., Kevlar): Uses aramid fibres. Known for exceptional impact resistance and toughness. Used in bulletproof vests, helmets, and protective gear.
- Natural Fibres (Jute, Hemp, Flax): Uses natural plant fibres. Known for being eco-friendly, biodegradable, and low-cost. Used in non-structural automotive panels and packaging.
4. Explain the properties and applications of polymer matrix composites.
Properties:
- Lightweight: They have a low density compared to metals.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: They are very strong for their weight.
- Corrosion-Resistant: They do not rust or corrode like many metals.
- Easy Fabrication: They can be easily molded into complex shapes, often reducing the number of parts needed.
- Low Cost: Generally cheaper to manufacture than metal composites.
- Electrical Insulation: Most polymer resins are good electrical insulators.
Applications:
- Automotive: Car body panels, bumpers, and interior components.
- Aerospace: Interior panels, luggage bins, and secondary structural parts.
- Sports Equipment: Tennis rackets, bicycle frames, bats, helmets, and golf clubs.
- Marine Industry: Boat hulls and superstructures.
5. Explain Matrix phase and Dispersed phase with example.
- Matrix Phase: This is the continuous, primary phase that surrounds and holds the other phase in place. It transfers the load to the reinforcement and protects it from the environment.
Example: In a fibreglass boat hull, the epoxy or polyester resin is the matrix phase. - Dispersed Phase (or Reinforcement): This is the discontinuous phase that is embedded within the matrix. Its primary role is to provide strength, stiffness, and other specific properties.
Example: In the same boat hull, the glass fibres are the dispersed phase.
6. (i) State reduced phase rule.
The reduced phase rule (or condensed phase rule) is used for systems where pressure is kept constant (condensed systems), ignoring the gas phase. The rule is:
6. (ii) Phase diagram of Lead-Silver system:
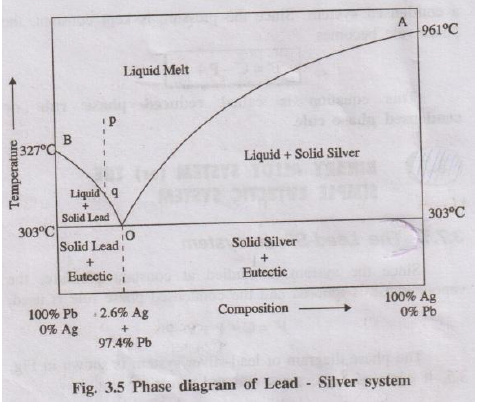
- Curve AO: This is the freezing point curve of Silver (Ag). As lead is added to silver, the melting point of silver decreases along this line.
- Curve BO: This is the freezing point curve of Lead (Pb). As silver is added to lead, the melting point of lead decreases along this line.
- Eutectic Point (O): This is the point where curves AO and BO meet. At this point, three phases (solid Pb, solid Ag, and liquid melt) coexist in equilibrium. The system is non-variant (F'=0). This occurs at a fixed temperature of 303°C and a fixed composition of 97.4% Pb + 2.6% Ag.
- Areas:
- Above AOB (Liquid Melt): Single phase, bivariant (F'=2).
- Area under AO (Liquid + Solid Ag): Two phases, univariant (F'=1).
- Area under BO (Liquid + Solid Pb): Two phases, univariant (F'=1).
- Below 303°C line: Two solid phases (Solid Pb + Eutectic) or (Solid Ag + Eutectic), univariant (F'=1).
6. (iii) Application in Pattinson's process:
The phase diagram explains the Pattinson's process for the desilverisation (removal of silver) of argentiferous lead (lead containing silver). When lead with a small amount of silver is cooled, pure lead crystallises out first (moving down from curve BO). This solid lead is removed, and the remaining liquid melt becomes progressively richer in silver, moving towards the eutectic point (O).
7. Applications and properties of composites
(a) Metal Matrix Composites (MMC):
- Properties: High strength and stiffness, excellent wear resistance, good thermal stability, and can operate at higher temperatures than polymer composites.
- Applications: Aircraft structural components, automotive engine parts (pistons, connecting rods), and brake discs.
(b) Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMC):
- Properties: Extremely high temperature resistance, high corrosion resistance, strong, but can be brittle (though tougher than traditional ceramics).
- Applications: Gas turbine engines (hot sections), aerospace thermal protection systems (space shuttle tiles), and biomedical implants.
(c) Hybrid Composites:
- Properties: Combine two or more different types of fibres (e.g., carbon and glass) in one matrix to get a balanced, cost-effective set of properties (e.g., stiffness from carbon, toughness from aramid).
- Applications: Sporting goods (skis, tennis rackets), military armour, and specialized automotive components.