Part B: 13-Mark Questions
1. Write a C program to find the sum of two numbers using a flowchart and algorithm.
Algorithm- Start
- Read two numbers: a, b
- Compute sum = a + b
- Display sum
- Stop
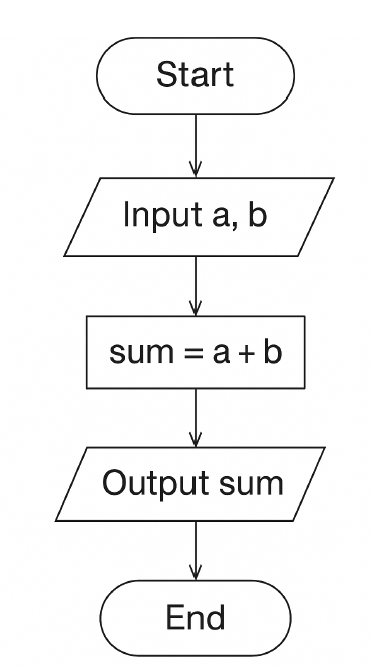 C Program
C Program
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number1;
int number2;
int sum;
printf("Enter the first integer: ");
scanf("%d", &number1);
printf("Enter the second integer: ");
scanf("%d", &number2);
sum = number1 + number2;
printf("\nThe sum of %d and %d is: %d\n", number1, number2, sum);
return 0;
}This program follows an Input-Process-Output (IPO) structure:
- Input: It uses
printfto prompt the user andscanfto read two integers, storing them innumber1andnumber2. - Process: It calculates the sum using the assignment statement:
sum = number1 + number2;. - Output: It uses
printfagain to display a formatted message showing the original two numbers and their calculated sum.
2. Elaborate the decision making and looping statements with suitable examples.
1. Decision-Making StatementsDecision-making statements are used to execute parts of code based on specific conditions.
- if statement: Executes a block if the condition is true.
if (x > 0) { printf("Positive number"); } - if-else statement: Executes one block if true, and another if false.
if (x % 2 == 0) { printf("Even"); } else { printf("Odd"); } - Nested if statement: An
ifstatement inside anotherifstatement.if (x > 0) { if (x < 10) { printf("x is between 1 and 9"); } } - if-else-if ladder: Used to check multiple conditions sequentially.
if (marks >= 90) printf("Grade A"); else if (marks >= 75) printf("Grade B"); else printf("Grade C"); - switch statement: Used for multiple choices based on a single variable.
switch (choice) { case 1: printf("Addition"); break; case 2: printf("Subtraction"); break; default: printf("Invalid choice"); }
Looping statements execute a block of code repeatedly.
- for loop (Entry-controlled):
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { printf("%d ", i); } // Output: 1 2 3 4 5 - while loop (Entry-controlled):
int i = 1; while (i <= 5) { printf("%d ", i); i++; } - do-while loop (Exit-controlled): Executes at least once.
int i = 1; do { printf("%d ", i); i++; } while (i <= 5);
3. i. Explain the general structure of a C program with an example.
ii. Write a C program to find the largest of three numbers using ternary operator.
i. General Structure of a C Program
A C program is organized into several sections:
- Documentation Section: Comments describing the program.
- Preprocessor Section: Includes header files (e.g.,
#include). - Global Declarations: Global variables and function prototypes.
- main() Function: The entry point where program execution begins.
- Subprograms / Functions: User-defined functions.
#include <stdio.h> // Preprocessor section
// Global declarations
int globalvar = 10;
void display(); // Function prototype
int main() { // main function section
int a = 5, b = 10; // Local declarations
int sum;
sum = a + b; // Statements
printf("Sum = %d\n", sum);
display(); // Function call
return 0;
}
// Subprogram / function
void display() {
printf("This is a user-defined function.\n");
}#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b, c, largest;
// Input three numbers
printf("Enter three numbers: ");
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
// Using nested ternary operator
largest = (a > b) ? ((a > c) ? a : c) : ((b > c) ? b : c);
// Output result
printf("Largest number = %d\n", largest);
return 0;
}Enter three numbers: 10 20 5
Largest number = 20
- First, it checks if
a > b. - If true, it checks if
a > c. If true,ais largest, elsecis largest. - If false (meaning
b >= a), it checks ifb > c. If true,bis largest, elsecis largest.
4. Explain the different types of loops in C with syntax.
Loops are used to execute a block of code repeatedly as long as a condition is true. C has three main types of loops:
1. for loop (Entry-controlled)Used when the number of iterations is known. The condition is tested before entering the loop.
Syntax:for (initialization; condition; update) {
// body of loop
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", i);
}
// Output: 1 2 3 4 5
Used when the number of iterations is not fixed. The condition is tested before the loop body executes.
Syntax:initialization;
while (condition) {
// body of loop
update;
}
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5) {
printf("%d ", i);
i++;
}
// Output: 1 2 3 4 5
The loop body is executed at least once because the condition is tested *after* the body executes.
Syntax:initialization;
do {
// body of loop
update;
} while (condition);
int i = 1;
do {
printf("%d ", i);
i++;
} while (i <= 5);
// Output: 1 2 3 4 5
5. Explain the all-looping statement with example.
Loops are used to execute a block of code repeatedly as long as a condition is true. C provides three main types of loops:
1. for loop (Entry-controlled)Used when the number of iterations is known. Condition is tested before entering.
Syntax:for (initialization; condition; update) { ... }
Example:
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", i);
}
// Output: 1 2 3 4 5
Used when iterations are not fixed. Condition is tested before executing.
Syntax:while (condition) { ... update; }
Example:
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5) {
printf("%d ", i);
i++;
}
// Output: 1 2 3 4 5
Executes at least once. Condition is tested after the body.
Syntax:do { ... update; } while (condition);
Example:
int i = 1;
do {
printf("%d ", i);
i++;
} while (i <= 5);
// Output: 1 2 3 4 5
C also has statements to control loop execution:
- a) break: Terminates the loop immediately.
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { if(i == 3) break; printf("%d ", i); } // Output: 1 2 - b) continue: Skips the current iteration and moves to the next.
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { if (i == 3) continue; printf("%d ", i); } // Output: 1 2 4 5 - c) goto: Transfers control to a labeled statement. (Use is generally discouraged).
int i = 1; loop: if(i <= 3) { printf("%d ", i); i++; goto loop; } // Output: 1 2 3
6. Explain the decision-making statement with an example.
Decision-making statements execute code based on conditions.
1. if statementExecutes a block if the condition is true.
Syntax:if (condition) { ... }
Example:
int x = 10;
if (x > 0) {
printf("x is positive");
}
// Output: x is positive
Executes one block if true, another if false.
Syntax:if (condition) { ... } else { ... }
Example:
int x = 5;
if (x % 2 == 0) {
printf("Even");
} else {
printf("Odd");
}
// Output: Odd
An if statement inside another if.
if (x > 0) {
if (x < 10) {
printf("x is between 1 and 9");
}
}
// Output: x is between 1 and 9
Used to check multiple conditions sequentially.
int marks = 80;
if (marks >= 90)
printf("Grade A");
else if (marks >= 75)
printf("Grade B");
else
printf("Grade C");
// Output: Grade B
Used for multiple choices on a single variable.
switch (choice) {
case 1: printf("Addition"); break;
case 2: printf("Subtraction"); break;
default: printf("Invalid choice");
}
// Output: Subtraction
7. Describe the structure of a C program with an example.
A C program follows a well-defined structure:
- Documentation Section: Contains comments (e.g.,
// Program to add two numbers). - Preprocessor Section: Includes header files (e.g.,
#include <stdio.h>). - Global Declaration Section: Declares global variables and function prototypes (e.g.,
int x;,void display();). - main() Function Section: Execution starts here. Contains declarations and statements.
int main() { int a, b, sum; printf("Enter two numbers: "); scanf("%d %d", &a, &b); sum = a + b; printf("Sum = %d", sum); return 0; } - Subprograms (Functions): User-defined functions written outside
main().void display() { printf("This is a function."); }
#include <stdio.h> // Preprocessor section
// Global Declaration
int globalvar = 10;
void display();
int main() { // main function section
int a, b, sum; // Declarations
printf("Enter two numbers: ");
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
sum = a + b;
// Statement
printf("Sum = %d\n", sum);
display(); // Function call
return 0;
}
// Subprogram
void display() {
printf("This is a user-defined function.\n");
}8. Explain about the various Decision making and branching statement with example.
Decision-making statements alter the flow of program execution based on conditions, allowing the program to "decide" which code to run.
1. if statementExecutes a block if the condition is true.
Syntax:if (condition) { ... }
Example:
int x = 10;
if (x > 0) {
printf("x is positive");
}
// Output: x is positive
Executes one block if true, another if false.
Syntax:if (condition) { ... } else { ... }
Example:
int x = 5;
if (x % 2 == 0) {
printf("Even");
} else {
printf("Odd");
}
// Output: Odd
An if statement inside another if.
if (x > 0) {
if (x < 10) {
printf("x is between 1 and 9");
}
}
// Output: x is between 1 and 9
Used to check multiple conditions sequentially.
int marks = 80;
if (marks >= 90)
printf("Grade A");
else if (marks >= 75)
printf("Grade B");
else
printf("Grade C");
// Output: Grade B
Used for multiple choices on a single variable.
switch (choice) {
case 1: printf("Addition"); break;
case 2: printf("Subtraction"); break;
default: printf("Invalid choice");
}
// Output: Subtraction